What is Fertilizer

What is Fertilizer
Fertilizer refers to any natural or synthetic substance added to soil or plants that contains essential nutrients required for plant growth. Fertilizers are materials applied to soil or plant tissues to supply essential nutrients that aid in plant development. The primary goals of using fertilizers are to improve soil fertility, provide necessary nutrients to plants, and enhance the yield and quality of agricultural products
Fertilizers can be produced in two forms: natural and synthetic. The primary nutrients present in fertilizers are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), commonly known as NPK. These macronutrients play vital roles in various plant functions, including
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for the growth of leaves and stems.
- Phosphorus (P): Crucial for root development, flowering, and seed production.
- Potassium (K): Supports strong stem growth and regulates water movement within plants.
In addition to the primary macronutrients, fertilizers may also contain secondary macronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, along with micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc, which are required in smaller amounts but are essential for plant health
Fertilizers act as a source of nourishment for plants and are primarily responsible for supplying essential nutrients. They are rich in compounds beneficial for plant growth and development
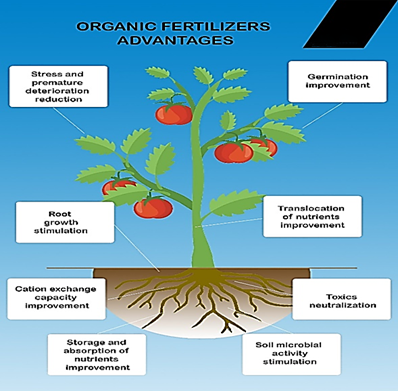
Figure 1.effects of fertilizer on plants
:Reasons for Using Fertilizers
- :ImprovementofSoilHealth
Fertilizers not only provide immediate availability of nutrients but also contribute to the long-term health of the soil by supplying essential elements required for plant nutrition. Fertilizers can enhance microbial activity in the soil, which plays a vital role in nutrient cycling and overall soil fertility. The organic matter present in fertilizers not only supplies nutrients but also improves soil fertility over time by increasing organic content and water retentioncapacity
Regular application of fertilizers helps to maintain and improve the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil. This practice prevents soil exhaustion and enhances its fertility
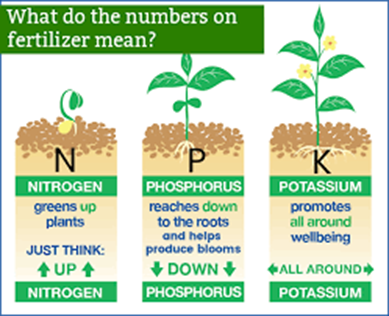
Figure 2 .Macronutrients
:2.NutrientSupply
Fertilizers provide essential nutrients required by plants and ensure proper nutrition by adding these elements to the soil. These nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which are vital for plant growth. Plants need a variety of nutrients, including macronutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), as well as micronutrients like magnesium, calcium, and iron. These nutrients are critical for various physiological processes including photosynthesis, root development, and fruit production
:3.EnhancementofGrowthandYield
Fertilizers enhance plant growth by supplying essential nutrients that may be deficient in the soil. This leads to improved flowering, fruiting, and overall plant health. Healthy plants exhibit greater resistance to pests and diseases, thereby contributing to increased agricultural productivity

Figure 3. Increasing crop growth and yield
EconomicBenefits
Efficient use of fertilizers can improve farmers’ profitability by increasing crop yield while minimizing waste
:SoilNutrientDeficiency
Symptoms of nutrient deficiency in plants may manifest as changes in leaf color and shape, deformation of stems and fruits, and the dropping of young buds. These deficiencies occur when plants are unable to obtain adequate nutrition, either due to a lack of nutrients in the soil or the plant’s inability to absorb available nutrients. Factors such as soil pH, temperature, moisture, and frost can influence nutrients availability and uptake

Figure 4.Correct fertilization method
:MechanismofFertilizereffectiveness
Fertilizers are essential for enhancing plant growth by supplying vital nutrients. The synthesis of fertilizers primarily involves three key macronutrients: nitrogen(N),phosphorus(P),and potassium (K). Each nutrient undergoes a distinct production process involving various chemical reactions and raw materials
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen promotes the growth of shoots and leaves and increases the green coloration in plants. It also accelerates seed germination, enhances photosynthesis, and ultimately improves crop quality. Nitrogen deficiency is mostly indicated by changes in leaf color
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus plays a role in cell division, lipid production, albumin synthesis, and photosynthesis. By helping plants absorb and utilize nutrients more effectively, phosphorus supports root, flower, and fruit growth, as well as grain filling. Additionally, phosphorus helps plants overcome environmental stresses by reducing stress impacts, aiding resistance to shocks. Phosphorus deficiency weakens roots and hinders flowering and fruiting in trees
- Potassium (K): Potassium contributes to overall plant growth and strengthening. Through its influence on protein synthesis, potassium helps to improve quality-related traits such as size, color, shape, and taste. It also enhances plant resistance to cold, drought, pests, and diseases. Potassium deficiency is evident through discoloration and yellowing of leaves
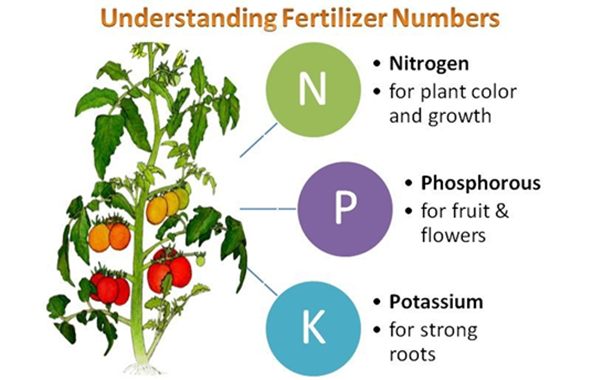
Figure 5.The effectiveness of fertilizer on plants
Application of Fertilizers in Agriculture
- :NutrientSupply
Fertilizers support plant growth by supplying essential nutrients and enhancing soil fertility IncreasingCropYield
By providing the nutrients required for optimal plant growth, fertilizers play a vital role in boosting agricultural productivity - :SoilHealthMaintenance
Fertilizers contribute significantly to improving soil health, which is essential for sustainable agriculture and maintaining ecological balance. They provide the necessary nutrients that plants require for proper growth and development
:DiseaseControl
Fertilizers play an important role in improving plant health and managing diseases. Appropriate use of fertilizers can significantly reduce the incidence and severity of various plant diseases by ensuring the availability of essential nutrients, which in turn promotes stronger growth and greater plant resilience
:StressResistance
Fertilizers are crucial in enhancing plant resistance to both abiotic and biotic stresses. This response is largely attributed to the nutrients they supply, which are essential for various physiological and biochemical processes in plants
:StrengtheningPlantCellsandCellWalls
Fertilizers contribute to plant health by influencing the structure and integrity of plant cell walls. Their effectiveness is linked to the availability of key nutrients that support the formation and maintenance of strong cell walls. By supplying vital nutrients, fertilizers strengthen plant cells and their walls, promote growth, and improve resilience against environmental stresses
:WaterBalanceRegulationinPlants
Fertilizers play an important role in maintaining water balance in plants, primarily by influencing nutrient availability and plant physiological responses
:RegulationofPlantGrowthandDevelopment
Fertilizers are vital for enhancing plant growth and development by providing essential nutrients that may be deficient in the soil
:Types of Fertilizers
:Based on Nutrient Composition
:NitrogenFertilizers
:These fertilizers are crucial for plant growth, especially for leafy vegetables and grasses. Types of nitrogen fertilizers include
:AmmoniumNitrogenFertilizers
These include ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium chloride. They supply nitrogen in a form readily available to plants
:NitrateNitrogenFertilizers
These consist of sodium nitrate and calcium nitrate, which are highly water-soluble and preferred by many crops due to their rapid availability
:AmideNitrogenFertilizers
Amide nitrogen fertilizers deliver nitrogen in the form of an amide group .The most common and widely used amide nitrogen fertilizer is urea, which contains a high nitrogen content (46%). Urea is essential for vegetative growth, increased greenness, and protein production
Before uptake by plants, these fertilizers must first be converted by soil microbes into ammonium carbonate and then into nitrate, making them available for plant absorption
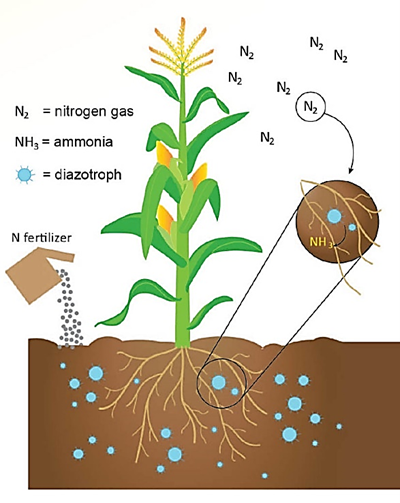
Figure 6.The effect of nitrogen fertilizer
:PhosphateFertilizers
Phosphate fertilizers contain phosphorus (P), which is essential for plant growth and development. Phosphorus plays a critical role in photosynthesis, energy transfer, root and fruit development. These fertilizers help to increase both the quantity and quality of crops, enhance plant resistance to stresses and diseases, and improve soil structure. Common types include Single Superphosphate (SSP), Triple Superphosphate (TSP), and Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) or Diammonium Phosphate (DAP)
Phosphate fertilizers are also known as chemical phosphorus fertilizers and contain various forms of phosphorus to increase the availability of this vital nutrient in the soil and support plant nutrition
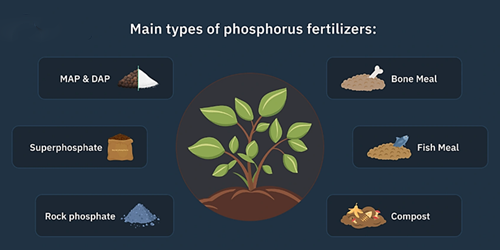
Figure 7.The effect of phosphate fertilizer
:PotassiumFertilizers
Potassium fertilizers are sources of the essential element potassium (K) necessary for plant growth. They come in various forms, including potassium sulfate (Solupots), potassium nitrate, potassium chloride, and liquid fertilizers. These fertilizers are used in agriculture to enhance plant resistance to environmental stresses such as drought, improve crop quality, increase the uptake of other nutrients, and support cell structure. Potassium fertilizers play a crucial role in promoting plant growth and development
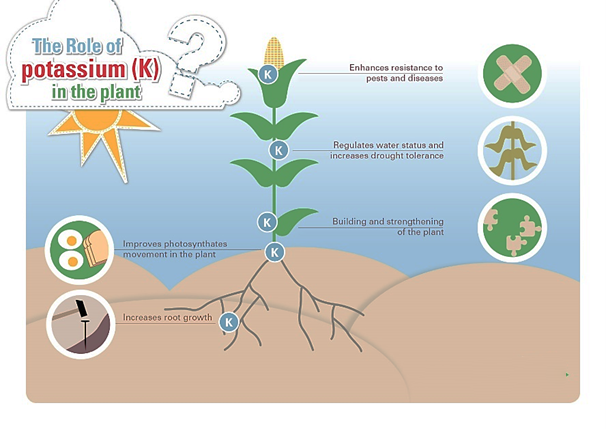
Figure 8.How potassium fertilizers work
:MicronutrientFertilizers
Micronutrients are elements that plants require in very small amounts (usually less than 0.01%), but their presence is essential for completing vital physiological processes in plants. Deficiency of even one of these elements can lead to reduced growth, lower yield, and increased susceptibility to diseases. These elements include boron (B), chlorine (Cl), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), zinc (Zn), and nickel (Ni). Although needed in small quantities, they are critical for plant nutrition and productivity
:SecondaryMicronutrientFertilizers
These fertilizers include sulfur, magnesium, and calcium, which are often combined with essential macronutrient fertilizers

Figure 9. Secondary micronutrient fertilizers
- :Based on Source
:OrganicFertilizers
These fertilizers are derived from natural sources and improve soil health by enhancing microbial activity. Organic fertilizers are products obtained from natural materials containing essential nutrients for plants. They originate from plant-based or animal-based sources
- Plant-based: Examples include compost, alfalfa meal, and liquid kelp
- Animal-based: Examples include manure, bone meal, and fish emulsion
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly to plants and improve soil health and structure over time. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, organic fertilizers increase soil biological activity and promote a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening and agriculture

Figure 10. Organic fertilizers
:MechanismofOrganicFertilizers
Organic fertilizers are produced through composting and fermentation processes, which can increase the presence of humic acids. The aerobic fermentation process stimulates microorganisms to decompose organic matter and release nutrients (P, N, and K) that are beneficial for crop growth
:Advantages of Organic Fertilizers
- :ImprovementofSoilStructure
Organic fertilizers increase soil permeability, improve aeration, and enhance water retention capacity. By increasing the organic matter content, they reduce soil compaction and create more pore spaces, which facilitate better air exchange and ventilation - :Long-termSustainability
Organic fertilizers release nutrients gradually, providing a sustained impact on soil quality and plant growth. The slow release of nutrients ensures their continuous availability to plant roots throughout the growing season and helps prevent nutrient leaching - :StrengtheningPlantRoots
By enriching the soil near plant roots, organic fertilizers enhance root structure and support overall plant growth - :ResistancetoDroughtandDiseases
Organic fertilizers contribute to combating drought, flooding, and certain plant diseases by improving soil health and plant resilience
:Types of Organic Fertilizers
:Plant-based Fertilizers
- Compost: Decomposed organic materials such as kitchen waste, yard debris, and leaves
- Green Manure: Cover crops (e.g., clover, alfalfa) that are grown and then incorporated back into the soil
- Seaweed: Rich in micronutrients and growth hormones
- Alfalfa Meal: Supplies nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
:Animal-based Fertilizers
- Manure: From cows, horses, chickens, or rabbits (should be composted to eliminate pathogens)
- Bone Meal: High in phosphorus and calcium, beneficial for root growth
- Blood Meal: Rich in nitrogen, promotes leaf growth
:How to Use Organic Fertilizers
- :SoilAmendment
Mix organic fertilizers into the soil before planting to improve soil fertility - :CompostTea
Steep compost in water to create a liquid fertilizer - :Mulching
Use organic materials such as straw or leaves as mulch to retain moisture and add nutrients to the soil - :Mineral(Chemical)Fertilizers
Mineral or chemical fertilizers are those produced industrially in factories through chemical processes. These fertilizers contain one or more essential nutrient elements for plants, converted into forms that are readily absorbable by roots (usually as water-soluble salts). They are synthetic fertilizers that provide nutrients in concentrated forms, including nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium fertilizers - Inorganic or synthetic fertilizers are chemicals derived from natural elements. Their primary goal is to meet the nutritional requirements of plants. The advantages of these mineral fertilizers include cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and rapid availability to plants

Figure 12.How organic fertilizers affect the plant
?WhyAreChemicalFertilizersUsed
Fertilizers maximize crop yield. Proper use of chemical fertilizers can significantly increase productivity. Chemical fertilizers are widely used in agriculture to enhance plant growth by supplying essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Compared to organic or biofertilizers, single-nutrient chemical fertilizers are relatively inexpensive
:AboutFaghihiIndustrialManufacturingCompany
Faghihi Industrial Manufacturing Company(FIMACO) specializes in producing various types of macro, micro, organic, and biological fertilizers. Our goal is to develop innovative fertilizers that improve both the quality and quantity of agricultural products
- Macro Fertilizers: Vigor Rooting, Vigor Stimulator, Vigor Exproma, and etc
- .Micro Fertilizers: Vigor Multi, Iron Chelates, Vigor Carbocop
- .Foliar Fertilizer: Vigor Foliage
- Water and Irrigation Fertilizer: Green Foliage
- .Supplementary Fertilizer: Vigor Anti
- .Organic Fertilizers: Bat Manure, Chicken Manure, Stimulator





